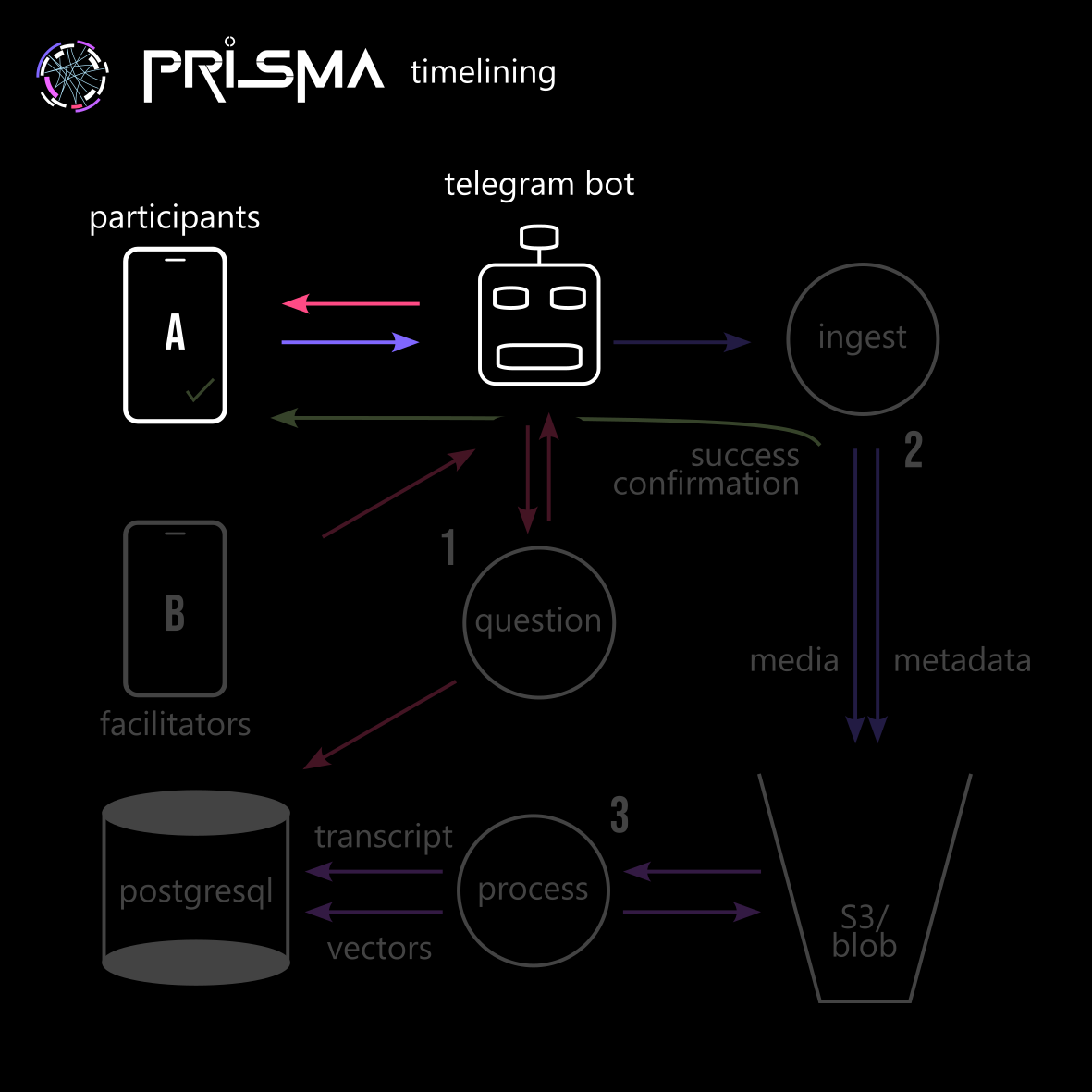
Overview¶
-
FastAPI Webhook Endpoint:
- We use FastAPI to create the webhook endpoint where Telegram will send updates.
- The endpoint is defined as a POST method that accepts the incoming data and processes it using the python-telegram-bot library.
-
Asynchronous Bot Initialization:
- Instead of relying on global bot initialization, we initialize the bot asynchronously within the webhook handler function.
- This is necessary because the
Applicationclass frompython-telegram-botneeds to be properly initialized before processing updates.
-
Using
Application.builder().token(TOKEN).build():- The bot is instantiated within the handler for each request using the
builder()method. - The bot is configured with the Telegram bot token stored in environment variables.
- The bot is instantiated within the handler for each request using the
-
initialize()Method:- The
initialize()method is called asynchronously to ensure the bot is fully initialized before handling updates.
- The
-
Pydantic Model for Request Validation:
- We use Pydantic models to validate and parse the incoming webhook data (e.g.,
update_id,message, etc.). - This ensures the data conforms to the expected structure and provides type safety.
- We use Pydantic models to validate and parse the incoming webhook data (e.g.,
-
Handling Incoming Messages:
- We define an
asyncfunction,handle_message(), which is used as a message handler for incoming text messages. When a message is received, the bot replies with a confirmation ("Received!").
- We define an
Received webhook update: {'update_id': 482821758, 'message': {'message_id': 46, 'from': {'id': 5165109192, 'is_bot': False, 'first_name': 'Tabs', 'username': 'tbsfchnr', 'language_code': 'es'}, 'chat': {'id': 5165109192, 'first_name': 'Tabs', 'username': 'tbsfchnr', 'type': 'private'}, 'date': 1741272018, 'text': 'yo'}}
-
Deployment on Vercel:
- The FastAPI app is deployed to Vercel, with the correct configuration and environment variables.
- The
vercel.jsonfile ensures that the serverless function is set up properly.
-
Webhook URL:
- The Telegram bot's webhook is set to the URL provided by Vercel after deployment.
- Vercel will route incoming requests to your serverless function endpoint (
/).
Code Example¶
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from telegram import Update
from telegram.ext import Application, MessageHandler, filters, CallbackContext
import logging
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from pydantic import BaseModel
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
TOKEN = os.getenv("TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN")
# Setup logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
# FastAPI app initialization
app = FastAPI()
# Pydantic model to match Telegram's update data structure
class TelegramUpdate(BaseModel):
update_id: int
message: dict
# Telegram message handler
async def handle_message(update: Update, context: CallbackContext) -> None:
"""Process incoming messages."""
logging.info(f"Received message: {update.message.text}")
await update.message.reply_text("Received!")
@app.post("/")
async def webhook(update: TelegramUpdate):
"""Process incoming updates from Telegram."""
try:
# Initialize the Telegram bot application
bot_app = Application.builder().token(TOKEN).build()
# Initialize the application asynchronously
await bot_app.initialize()
# Log the incoming update for debugging
logging.info(f"Received webhook update: {update.dict()}") # Log incoming data
# Convert the incoming update to the correct format for python-telegram-bot
telegram_update = Update.de_json(update.dict(), bot_app.bot)
# Add message handler
bot_app.add_handler(MessageHandler(filters.TEXT & ~filters.COMMAND, handle_message))
# Process the update (this is needed to trigger the message handler)
await bot_app.process_update(telegram_update)
return {"status": "ok"}
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error processing request: {str(e)}")
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
Key Configuration¶
-
Environment Variables:
- Store your
TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKENin a.envfile or directly as Vercel environment variables.
- Store your
-
vercel.jsonConfiguration: Ensure yourvercel.jsonlooks like this for correct deployment:{ "version": 2, "builds": [ { "src": "api/webhook.py", "use": "@vercel/python" } ], "env": { "PYTHON_VERSION": "3.12" } } -
Telegram Webhook URL:
-
Set the webhook URL for your bot in Telegram:
https://<your-vercel-url>/webhook
-
Conclusion¶
- This setup leverages FastAPI for handling requests and python-telegram-bot for interacting with the Telegram Bot API.
- It ensures asynchronous initialization of the bot for each webhook request, making it efficient for serverless deployments.
- The
initialize()method ensures proper setup of the bot on each request, avoiding issues with uninitialized bot instances. - Logging and Pydantic models help with debugging and validating the incoming webhook payloads.